IF CLAUSES / CONDITIONAL CLAUSES (Type 2)
Conditional clauses consist of two sentences. One is a clause that starts with if, which is called as ‘if clause’. The other is called the Main clause. Each sentence has a verb. It is important to know which tenses are to be used in these clauses and they play a big role in determining the meaning of the sentence.
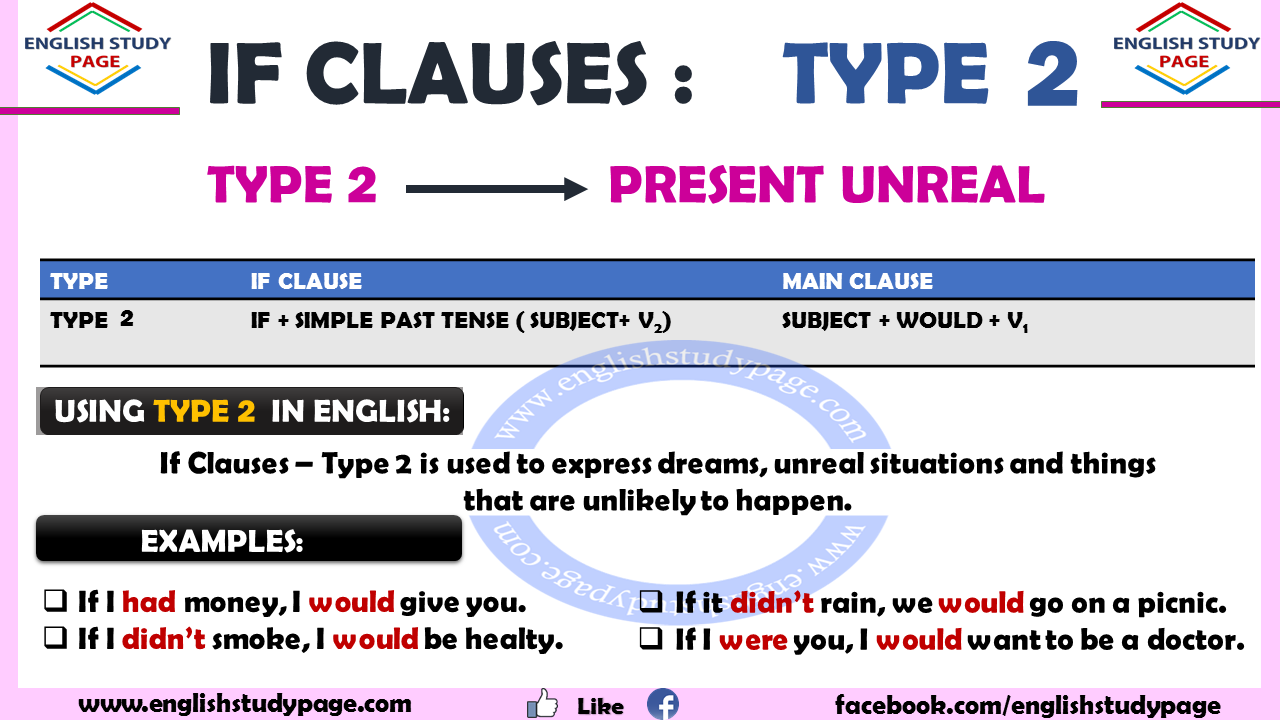
Detailed information for the type 2 is given below:
Form of The Type 2 :
The tense in if clause is generally simple past tense; the tense in main clause is generrally would although there are different uses which we will specify below.
| Type | If clause (condition) | Main clause (result) |
| Type 2 | If + Simple past Past Continuous Past Modals (could, had to…) | would could + V1 or be + V-ing might |
Using Type 2:
The conditional sentences indicate us a possible condition and its probable result. It means that the expected actions depends on a condition. If Clauses – Type 2 is used to express dreams, unreal situations and things that are unlikely to happen. In other words, The condition specified in the clause is not actual but is a condition that is currently being imagined. Although the verb is used in the past, we use type 2 when talking about present time or now.
- If I had money (if clause), I would give you(main clause). ( but I don’t have money)
- If she knew the answer, she would win the prize. ( but she doesn’t know the answer)
- If I didn’t smoke, I would be healty. ( but I smoke so I am not healty)
- If he had enough experience fort he job, the boss could hire him. ( but he doesn’t )
- If I had your phone number, I would call you. ( but I don’t have your phone number)
- If you came to the party, we would have a lot of fun. ( but you don’t come to the party)
- If I were a rich man, I would buy a home like palace. ( but I am poor)
- If I could speak english very well, I would look for a job in foreign companies. ( but I can’t)
- If he had time, he would study well for his exam. ( but he doesn’t have time)
- If it didn’t rain, we would go on a picnic. ( but it is raining)
- If my house was in the forest, I would walk constantly in the green. ( but my house doesn’t in the forest)
- If I were you, I would want to be a doctor. ( but I am not you)
- If I understood what the teacher said, I could tell you. ( but I don’t understand )
- If she weren’t ill, she would go to the school. ( but she is ill )
- If I were a chairman, I would offer new and different ideas. ( but I am not chairman)
- If you participated in the election, people would choose you. ( but you don’t participate )
Notes:
1. The sentence can begin with an if clause or a main clause. If the sentence begins with an ‘if clause’, put a comma between the if clause and the main clause.
If + past tense, or could + (,) + present unreal conditional ( would or modals )
Present unreal conditional ( would or modals ) + if + past tense, or could
- If I went to Paris, I would see the Eiffel Tower. / I would see the Eiffel Tower if I went to Paris.
- If you had a n invitation card, you should go to the party. / You should go to the party if you had an invitation card.
- If we used the time properly, we would finish our project. / we would finish our project if we used the time properly.
2. If you want, we can use modals in both ‘ıf clause’ and ‘main clause’ or you can use modals only in one part.
- If I had enough experience fort he job, the boss could hire him.
- If I could speak english very well, I would look for a job in foreign companies.
- If I understood what the teacher said, I could tell you.
3. In ‘If Clauses Type 2’, we usually use ‘were’ which is past form of ‘to be’ instead of ‘was’ although the pronoun is ‘I, he, she or it’.
- If I were you, I wouldn’t marry with him.
- If she were ill, she couldn’t attend the meeting.
- If it weren’t snowy, I would go out.
4. In Type 2, one or two of the clauses can be negative
- If I woke up late, I wouldn’t I be aware of what happened.
- If my mother did not remind me, I would forget my worksheet at home.
- If she were angry, she wouldn’t not talk to us.
5. Using Type2 in questions
- What would happen if humans disappeared?
- What would we do firstly if a fire broke out?
- Would you cry if he left you?
- What would happen if you didn’t drink water?
- What would you do if you learned that you had a bad illness?
6. Tenses and structures can be used in If Clauses- Type 2 are given below:
In If Clause; past form of to be, past continuous tense, should, could and had to are also used.
- If you were clever, you would understand what I meant.
- If she were cooking, I would help her.
- If he could come here, they would show him something that you would like.
- If I had to attend to the meeting, I would miss the plane.
- If she should join us (were to join us), She wouldn’t be bored.
In Main clause; would, would be doing, could, would be able to, might ve would have to are also
used.
- If I had one more chance, I would try to find out where I made the mistake.
- If it weren’t important, I would not be looking for him right now.
- If I had a good education, I could apply for a job abroad.
- If he earned lots of money, he would be able to buy a new car.
- If we had time, we might get the course.
- If she did not finish the project, she would have to get up early today.
7. Would can be written short as ‘d’. You can always use this abbreviation.
- If you lost time, you would ( you’d ) miss the bus.
For Conditionals – Type 0, click here
For Conditionals – Type 1, click here
For Conditionals – Type 3, click here
For Conditionals – Mixed Type, click here

Best explanation till I have learned till now good luck with other grammar’s