USING “ALTHOUGH” VS “THOUGH“ VS “EVEN THOUGH“ IN ENGLISH
“Although“, “Though” and “Even though” are all subordinating conjuctions, which connect two sentences together.
Sentences with these conjuctions have two clauses; one “main clause” and the other “concessive clause” ( which include opposite idea (contrast) of the main clause of the sentence. )
“Although“, “Though” and “Even though” are used for the same meaning, expressing the idea of contrast. But structurally there is a small difference between them.
You can find detailed explanations and examples below.
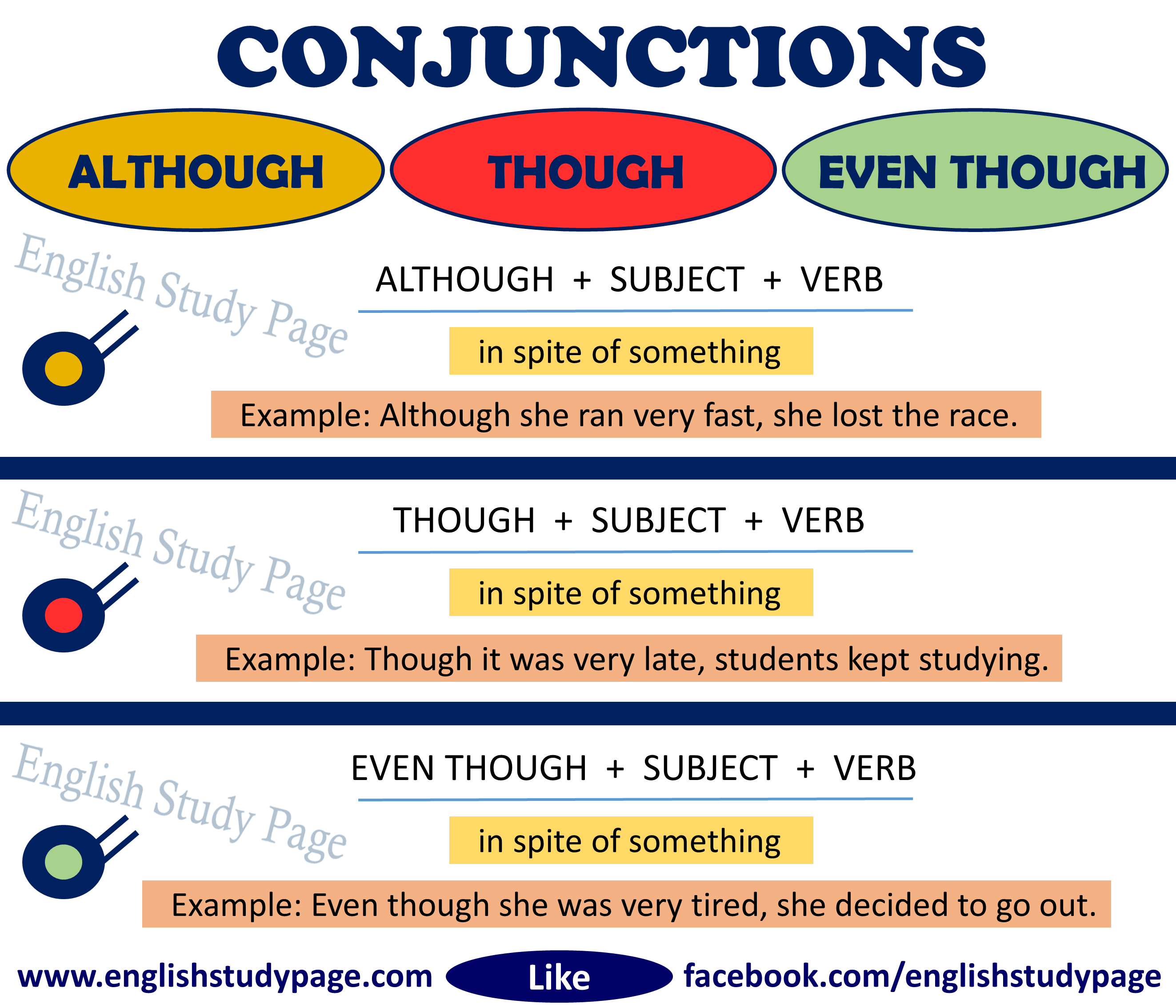
USING “ ALTHOUGH “ IN ENGLISH
“Although” means “in spite of something”.
Structure:
![]()
Examples:
- Although it rained all day, we enjoyed the party very much.
- He failed in the exam, although he studied very hard.
- Although she ran very fast, she lost the race.
- They didn’t go to the party, although they were invited.
USING “ THOUGH “ IN ENGLISH
“Though” means “in spite of something”. ( “Though” is informal way to say “Although” – the weakest expression or emphatic )
Structure:

Examples:
- Though the weather was very cold and snowy, the kids played outside.
- He isn’t happy, though he is rich.
- Though it was very late, students kept studying.
- She doesn’t want to go to the doctor ,though she is very sick.
Attention:
“Though” can be used at the end of a sentence.
Example:
- I agree that she is a good singer. I don’t like her, though.
USING “ EVEN THOUGH “ IN ENGLISH
“Even though” means “in spite of something”. ( “Even though” is more formal way to say “Although” – the strongest expression or emphatic )
Structure:

Examples:
- Even though they were millionaires, they drive old cars.
- We are still very hungry, even though we ate very much .
- Even though she was very tired, she decided to go out.
- He had a good time with his family, even though he was very busy yesterday.
AS A RESULT WE CAN SAY;
- There must be a contrast between two sentences. ( If the first sentence is positive, the second sentence should be negative in meaning. If the first sentence is negative, the second sentence should be positive in meaning.)
- As conjunctions, “although” , “though” and “even though” are interchangeable because these three conjuctions have the same meaning, but the most powerful expression ( most emphatic and formal ) is “Even though”. The weakest expression ( least emphatic and informal ) is “Though”.
- There may be different tenses between the sentences, which they connect. So while the first sentence is present, the second sentence may be past.
- “Though” can be used at the end of a sentence.
ATTENTION:
When the clause with although/though/even though comes before the main clause, we should put a comma at the end of the clause. When the main clause comes first, we don’t need to use a comma.
Examples:
- Even though I have many friends, I feel myself lonely.
- He was very energetic (,) although he was old.

It was a very useful and fruitful lesson for me. I have just made one more step at grammar. Now I am aware of difference among these similar conjuctions. Thank you.
I like this web page and so I am trying to improve my English skills.
This site is very useful for me to improve my English skill especially for the grammar
a millions of thanks to english study page
There is a mistake in your first example….run?
This site is very well structured and this topic helped me to step further with my grammar. Thank you