IF CLAUSES / CONDITIONAL CLAUSES (Mixed Type)
The conditional sentences indicate us a possible condition and its probable result. It means that the expected actions depends on a condition. Conditional sentences have two clauses. Until now, we have learned that two parts or clauses in conditional sentences have the same times.
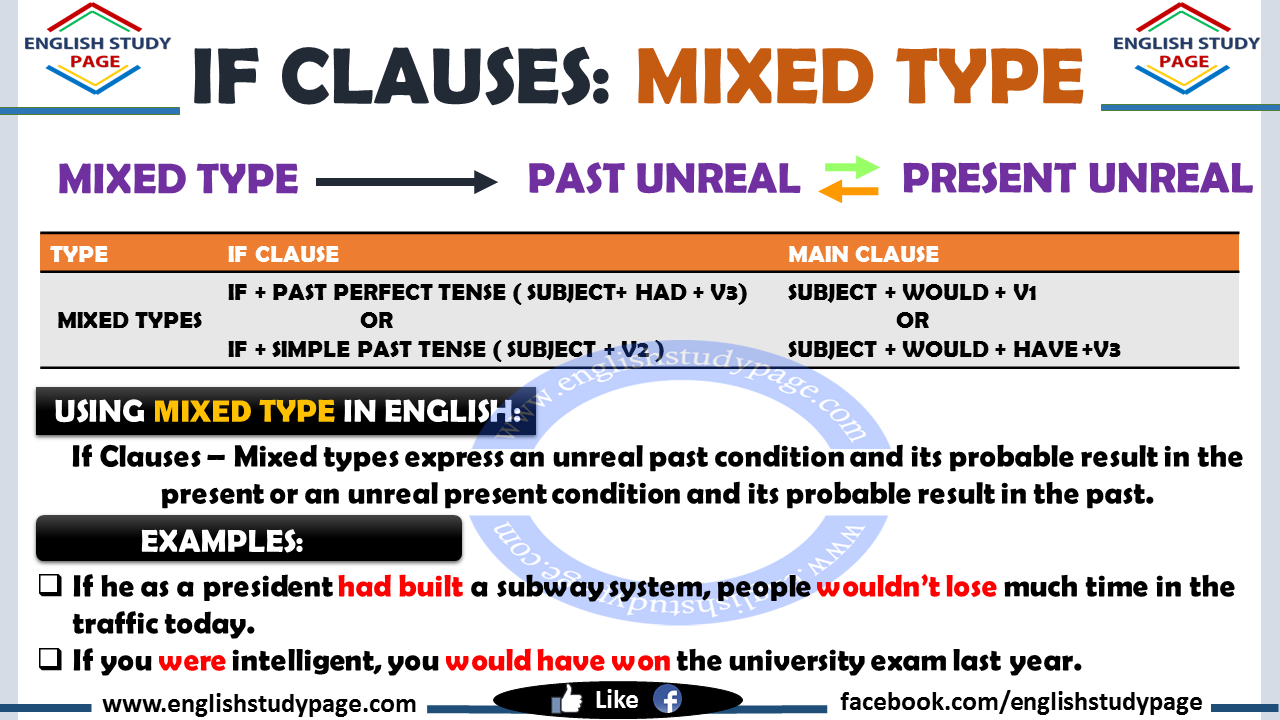
In some cases, unreal conditional sentences are mixed. Namely, the time in the If-Clause is not the same as the time in Main Cause. When it is so, these sentences or clauses are called mixed types or mixed conditionals.
There are two main types of mixed conditional sentences.
FORMS:
Shortly;
- Form: IF + TYPE 3 + TYPE 2 ( PAST CONDITION +PRESENT RESULT)
- Form: IF + TYPE 2 + TYPE 3 ( PRESENT CONDITION +PAST RESULT)
| Type | If clause (condition) | Main clause (result) | ||
Mixed type (1) |
If + | Past Perfect Past Perfect Continuous (PAST) |
Subject + | would could + V1 might(PRESENT) |
Mixed type (2) |
If + | Past Continuous Simple Past (PRESENT) |
Subject + | would could + HAVE + V3 might (PAST) |
Using Mixed Type 1: ( from PAST to PRESENT ) ( TYPE 3 + TYPE 2 )
If Clauses Mixed Type 1, is used to connect the past and the present. In other words, the time is the past ( past perfect tense ) in the ‘If clause’ and is the present (modal present ) in the ‘main clause’.
There is an unreal past condition and its probable result in the present.
- If he as a president had built a subway system, people wouldn’t lose much time in the traffic today.
- If she had passed the exam, she wouldn’t have to study now.
- If I had been born in England, I could speak English very well.
- If we hadn’t sold our house, we wouldn’t have to sit in a rental house now.
- If she had stayed with her mother, she would not feel so lonely.
- If Billy had called me, I would talk to him now.
- If the passenger had hurried, he would catch the train now.
Using Mixed Type 2: ( from PRESENT to PAST)
If Clauses Mixed Type 2, is used to connect the present and the past. In other words, the time is the Present ( simple past ) in the ‘If clause’ and is the past ( modal perfect ) in the ‘main clause’.
There is the past result of a present condition.
- If he were my real friend, he would have called me yesterday.
- If we saw him again, we would have told him the truth.
- If I had a lot of money, I wouldn’t have walked too much and I will take a taxi to the office.
- If you were intelligent, you would have won the university exam last year.
- If she trusted him, she would have married with him.
- If you weren’t afraid of me, you wouldn’t have tried to lie to me.
- If Marry liked Susan, she would have gone to the birthday party last night.
NOTES:
Although we say mainly used two types of mixed conditionals, we can see other types of mixed Conditionals (These structures are different from each other in terms of their meanings). Don’t forget that all mixed conditionals have two tenses. One is simple past tense or past continuous tense, the other is past perfect tense.
Just using time expressions, we can change the meaning of the clauses. These are given in sentences below.
- If we had decided which projects to apply yesterday, we would meet you tomorrow. (from PAST to FUTURE)
- If you weren’t a successful student, I wouldn’t take you to the cinema next week as a reward. (from PRESENT to FUTURE)
- If they weren’t coming us next week, We would have joined for a nice trip. ( from FUTURE to PAST)
- If Danny came with us to the concert tonight, we would be very happy. ( from FUTURE to PRESENT)
For Conditionals – Type 0, click here
For Conditionals – Type 1, click here
For Conditionals – Type 2, click here
For Conditionals – Type 3, click here

Hello! You are doing a great job with all this fantastic stuff for free here. I like your page. Thanks a lot. Robert